It is known that the effect and result of the use of Botox can be affected by antibiotics and some other drugs that the patient either takes during the procedure, or took shortly before botulinum therapy. Moreover, this is relevant not only for the use of Botox, but also for any botulinum toxin preparations, including Dysport, Xeomin, Mioblock and others.
The consequences of this effect can be quite noticeable: the effect of botulinum therapy either turns out to be unpredictably more pronounced than expected (up to the development of undesirable side effects), or, on the contrary, weakens so much that the procedure does not bring the desired cosmetic result. Moreover, some antibiotics so strongly affect the effect of botulinum therapy that taking them is a direct contraindication for botulinum toxin injections.
Next, we will consider what specific antibiotics can affect the results of Botox, what are the consequences of such an interaction of drugs and what other drugs are undesirable for botulinum therapy ...
The effect of antibiotics on the effect of Botox
Antibiotics do not directly affect botulinum toxin. They do not destroy it and do not affect its pharmacokinetics in the tissues, even if the concentration of a specific antibacterial agent in the injected muscle is high enough.
On a note
In principle, no antibiotic can act on a botulinum toxin molecule. The fact is that the mechanism of action of antibiotics is to suppress the vital activity of bacteria - pathogens of infections. Botulinum toxin is not a bacterium.
The compatibility problem between antibiotics and Botox, as well as other botulinum toxin preparations, is due to the fact that some antibacterial drugs have an effect similar to that of botulinum toxins. In particular, they reduce neuromuscular conduction and lead to muscle relaxation. Already under their influence, some facial muscles of the face, as well as the muscles of the neck, can relax, which leads to partial or complete smoothing of wrinkles.
If Botox is also added to the target muscles at this time, the effect may be excessive: a complete blockage of the innervation of the muscle fiber will occur, which will lead to undesirable phenomena - violation of facial expressions, facial symmetry, impaired articulation and diction.
Another undesirable phenomenon associated with taking such antibiotics is the difficulty in adequately assessing the strength of muscle contractions when planning Botox injections. A situation is possible when the muscles are somewhat relaxed under the influence of antibiotics, as a result of which, when evaluating wrinkles, the doctor decides to inject small doses, and after botulinum therapy, when the antibiotics end, the muscles will restore full tone, wrinkles will appear and it turns out that the dose was clearly insufficient.
Under the influence of certain antibiotics, the effect of Botox injections may increase uncontrollably, which in some cases leads to undesirable consequences.
It is important here that not all antibiotics affect Botox in the same or similar way. In itself, the weakening of neuromuscular transmission is a kind of side effect, which is manifested far from each of these funds. Therefore, it would be a mistake to believe that taking any antibiotics is a contraindication for botulinum toxin therapy. Below we will find out which of these drugs specifically change (or may change) the effect of “beauty injections”.
Now we emphasize that a similar effect that enhances the effect of botulinum toxin can be exerted by other drugs that also disrupt neuromuscular communication or otherwise affect muscle tone.
There are also funds that, on the contrary, weaken the effect of botulinum toxin. They either potentiate muscle tone in response to a nerve impulse, or they themselves stimulate muscle fiber contraction. Consequently, taking them during the period of botulinum therapy can lead to the fact that the effect of injections will be either less pronounced than expected, or it will not be at all.
The list of antibiotics that enhance the action of botulinum toxin
To date, the effect of the following antibiotics on the effect of Botox injections and other botulinum toxin preparations has been unequivocally proven:
- Aminoglycosides - streptomycin, gentamicin, tobramycin, neomycin, amikacin, kanamycin and others. Their side effects include neuromuscular blockade (sometimes very severe), sometimes leading to life-threatening consequences - apnea and cardiac arrhythmias. Similarly, these antibiotics affect the response of facial muscles to nerve impulses;
- Lincosamides - lincomycin and clindamycin. Similarly, they contribute to the relaxation of skeletal muscles and facial muscles, which can provoke an additive effect in parallel botulinum therapy;
- Macrolides - erythromycin, azithromycin, josamycin, spiramycin, midecamycin, clarithromycin, roxithromycin. Their relaxing effect is less pronounced than that of aminoglycosides, but is also able to manifest itself with botulinum toxin injections;
- Tetracyclines - known as side effects that can cause dysphagia (inability to take a sip). The same effect is sometimes manifested during botulinum therapy, and therefore, with the simultaneous use of tetracyclines and botulinum toxin, it is possible either to increase the severity of this effect, or to manifest it in cases where it would not have arisen with separate use of drugs;
- Polymyxins - their action is similar to that of tetracyclines.
A complete list of antibiotics that can enhance the action of botulinum toxin includes more than 100 items. Including, the most modern drugs from the above groups that have not yet entered mass production are included in this list.
It is not confirmed, but it is assumed that the action of botulinum toxin can enhance fluoroquinolones. These antibacterial agents are not antibiotics in the full sense of the word, since they have no natural analogues (all antibiotics are either natural substances or their derivatives). With the use of fluoroquinolones, myalgia and muscle weakness are often manifested, which is also the reason not to use them simultaneously with Botox injections.
Before the botulinum treatment procedure, it is important to notify your cosmetologist about which drugs are being taken or have been recently taken.
Feedback:
“I myself had such an unpleasant moment when, after the second time of injections, a terrible SARS developed, with snot and flu-like aches in the muscles. I call the doctor with this case, she says that there is no point in prescribing antibiotics, since the infection is probably viral. She said that if symptoms of a bacterial infection appear, then only antibiotics will be needed. She said it was safe. And then I read that people write ... I’ll tell you, it was really scary to read. Some write that the antibiotic completely erases the entire effect of Botox, as if nothing had been injected. Someone has been ringing in my ears for months after this, and someone has a terrible diarrhea. Manufacturers deny everything, write that it is all safe. But there are a lot of negative reviews. In general, I was lucky - after four days everything went. But if it didn’t pass, I don’t even know if I would drink these antibiotics or not ... ”
Ilona, from correspondence on the forum
Other pharmaceuticals that may have an undesirable effect with botulinum therapy
A similar effect, manifested in muscle relaxation and an unpredictable increase in the effect of botulinum toxin injections, is exerted by certain drugs whose active substances are derivatives of neurotoxins.
The most famous of them are curare-like muscle relaxants - derivatives of curare venom or close to it in nature. This poison acts in a manner similar to botulinum toxin, inhibiting the activity of neuromuscular synapses, although the effect of getting into the body is not as strong as the effect of poisoning with botulinum toxin.
On a note
Nevertheless, curare is considered one of the most powerful poisons in the wild, inferior in terms of toxicity except to botulinum toxin and batrachotoxin. In particular, curare venom, along with batrachotoxin, is used by South American Indians to lubricate arrowheads, which they use to hunt wild animals.
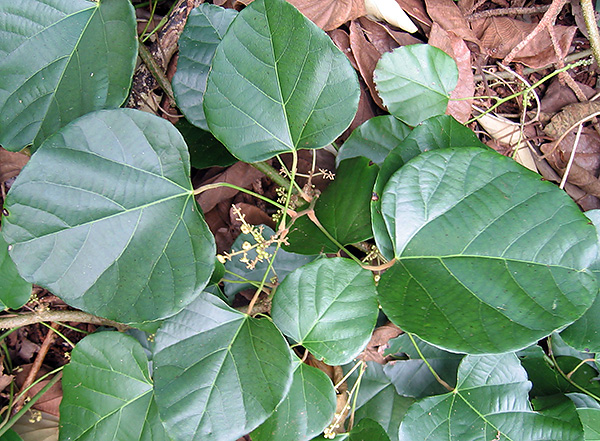

The plant Chondrodendron tomentosum is ubiquitous in South America and is the raw material for curare poison.
Curare-like drugs include:
- Tubocurarine chloride;
- Pipecuronium bromide;
- Pancuronium bromide;
- Dithilin;
- Prozerin;
- Metacin;
…and some others. When using them, botulinum therapy cannot be carried out.
Similarly, the effectiveness of botulinum toxin in cosmetic procedures may also be affected by agents specifically designed to reduce neuromuscular conduction. They are used for various purposes - relieving muscle spasms, treating lumbar radiculitis and some rheumatic diseases, relieving muscle tension during abdominal operations.
These include:
- Baclofen;
- Bendazole;
- Tizanidine;
- Tolperisone.
Some anxiolytics (drugs designed to eliminate anxiety and general relaxation) - Diazepam and Tetrazepam, Atarax can have a similar effect. It is also assumed that combined sedatives (e.g. Corvalol), blood anticoagulants, and drugs that increase the concentration of calcium inside the cells can enhance the effect of botulinum toxin. Of these, blood anticoagulants are contraindicated, including because Botox injections themselves can lead to edema and hematomas, and anticoagulant drugs can provoke or exacerbate these undesirable effects.
Botox-lowering drugs
On the other hand, there are drugs that increase the spasticity of the muscles, including the facial ones, even when taken orally. Due to this antagonistic effect, they can reduce the effectiveness of Botox injections up to the complete elimination of the effect of the latter.
For example, botulinum therapy is undesirable in the case of parallel or recently completed treatment of malaria with chloroquine or other derivatives of 4-aminoquinoline. Side effects of these drugs include seizures and cramping of various muscles, including skeletal and facial. Depending on the strength of such spastic phenomena, they can affect the adequacy of assessing the state of muscles before injections and provoke the doctor to administer more than necessary.
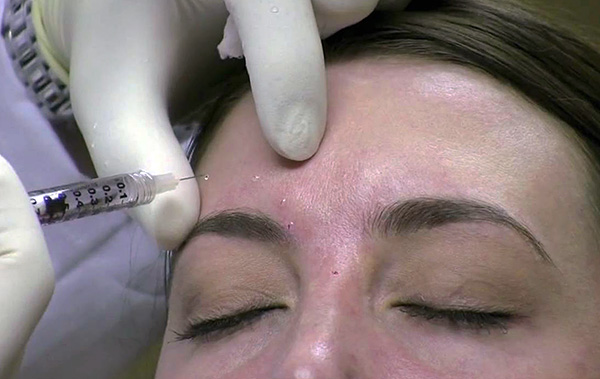
Botulinum toxin injection in the forehead and interbrow.
Similarly, taking medications from many other groups can lead to muscle cramps and cramps. In particular, such phenomena are described for certain hormonal preparations, certain antiviral agents, antidepressants and antibiotics, which are generally not contraindicated during botulinum therapy, but in individual cases may cause cancellation or transfer of procedures.
For example, the antiherpetic drugs Acyclovir, Valtrex and Famciclovir can not be drunk either immediately before injections of Botox or its analogues, or immediately after them. Among the side effects of these agents, muscle cramps are also indicated.
When can I use Botox after taking antibiotics?
For each type of antibiotic, a period is regulated, after which, after its use, injections of botulinum toxin can be done. For most drugs of the aminoglycoside, macrolide and tetracycline groups, this period is about 14-21 days (2-3 weeks). During this time, the substance is completely excreted from the body, and its effect is completed, therefore, it will not affect the result of Botox injections.
At the same time, some antibiotics are eliminated from the body faster (within 2-3 days), while others may be contained in tissues in high concentrations for several months. Therefore, it is extremely important for a cosmetologist to know what specific drug was taken by his patient in order to set a date for the procedures.
Also, when assessing the timing of the possible use of botulinum toxin, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient's body - gender and age, body weight, sensitivity to a specific antibiotic and botulinum toxin drug. All of them can both reduce and increase the period after which botulinum therapy can be carried out.
On a note
The instructions for botulinum toxin preparations do not clearly indicate how many days after antibiotics can be injected. The decision on the admissibility of the procedure is made by a cosmetologist.

In any case, the patient must understand that the priority of Botox injections is always lower than the priority of antibiotic treatment. Health depends on adequate antibiotic therapy, and sometimes even life, and practically nothing depends on whether the patient has a wrinkle for a week or two.
Therefore, the desire to run for Botox injections is completely unjustified, not yet completing the course of taking an antibiotic or any other medicine - an antidepressant, an anticoagulant of blood or any other, that is, in fact, has not yet recovered from a serious illness. It would be more correct to first fully recover and allow the body to regain strength, and then plan cosmetic procedures.
Drugs whose effect on the effect of botulinum therapy is not confirmed or is absent
Also, very often patients ask whether they can inject botulinum toxin when taking certain drugs, if these drugs are not listed in the list of contraindications for botulinum therapy. Such a safety net is quite justified, but in most cases and for most medicines even a doctor cannot give a definite answer.
To date, a list of approximately 370 drugs has been compiled, the simultaneous use of which with botulinum toxin is not recommended. This list is constantly updated and updated as new data and new precedents emerge. A cosmetologist conducting Botox injections always considers this list and before the procedure finds out if the patient is using such drugs.
There are hundreds of drugs whose use is a contraindication to Botox injections, and this list is periodically expanding.
However, in some cases, even approved drugs can interact with botulinum toxin or affect its effect in an undesirable way. This is a consequence of the individual characteristics of the body, and it is impossible to foresee some of these reactions. Fortunately, most of these reactions are minor, and the undesirable effects that occur are quickly resolved.
Some means are considered below, the possibility of simultaneous administration of which with botulinotherapy is of most interest to patients:
- Penicillin antibiotics - in fact, penicillin, amoxicillin (Amoxiclav and others), ampicillin, bicillins. They do not affect neuromuscular transmission, and therefore, taking them is not a clear contraindication for botulinum therapy.But, again, it is somewhat unreasonable to "race to Botox", being sick and continuing to take pills of these funds;
- Paracetamol and Diclofenac also do not exclude the use of botulinum toxin, but, like antibiotics, it is not advisable to do cosmetic procedures when the patient has a high temperature and the body is weakened;
- Afobazole - despite the fact that this remedy belongs to anxiolytics (tranquilizers), it does not cause muscle weakness and does not enhance the effect of botulinum toxin. Therefore, taking it is not a contraindication for botulinum therapy;
- Reduxin - a means for weight loss. Among its side effects, convulsions are indicated, but its reception is not a definite factor excluding Botox injections. The doctor should independently assess the condition of the patient taking Reduxin and decide whether he should inject botulinum toxin;
- Various hormonal drugs, including oral contraceptives - due to differences in their action, it is impossible to unambiguously characterize the admissibility of their intake with the use of botulinum toxin - it all depends on the specific drug;
- Local antibiotics - as a rule, these drugs do not have a systemic effect. If they are not used to treat skin infections in places of alleged injections, then with their use Botox can be used;
- Mexidol - is able to exert an anticonvulsant effect, enhancing the effect of botulinum toxin;
- Antifungal drugs - sometimes they can cause unwanted side effects, but there are no general rules on the possibilities of their use in botulinum therapy.
In general, given the safety of the procedures for the introduction of botulinum toxin itself, in most cases Botox is safely administered with the parallel use of drugs that are not on the list of clearly contraindicated botulinum toxin therapy.
What to do to a patient taking certain drugs before injections of botulinum toxin?
The main thing that the patient should remember: the decision on the possibility of using botulinum toxin during the use of certain drugs should be made (and will ultimately be made) by the doctor only. Therefore, it makes little sense to seek out information and find out the compatibility of Botox and those or other means: the procedure will take place or not take place, depending on what the cosmetologist decides.
It is important to understand that when making a decision, a good doctor will evaluate not only universal contraindications and limitations, but also the individual characteristics of a particular patient, their tolerance to certain drugs, the presence of allergic reactions in history and many other data. As a result, those conclusions that the patient will make at home according to information from the Internet, in reality, may not correspond to the decision made by the doctor.
And in any case, you should always remember that there is no urgency in injecting botulinum toxin. If the patient is being treated for a particular disease and takes drugs that may be incompatible with Botox or its analogues, it will be as safe as possible to simply end the therapy and only then carry out cosmetic procedures. It will be safer and more efficient.
Contraindications to the use of Botox: comments of a cosmetologist
Useful video about possible complications after botulinum toxin injections